The Complete Guide to Mind Mapping: Visual Thinking for Enhanced Learning and Productivity
Mind mapping has revolutionized how millions of people organize information, solve problems, and unleash their creative potential. This powerful visual thinking technique transforms the way we process and retain complex information by leveraging our brain’s natural ability to think in patterns and associations.
What is a Mind Map?
A mind map is a visual thinking tool that helps organize information in a hierarchical and interconnected way. Unlike traditional linear note-taking methods, mind maps mirror how our brains naturally process information—through associations, connections, and visual patterns. The technique starts with a central concept placed in the middle of a page, with related subtopics branching outward like the branches of a tree or neurons in the brain.
Originally developed by British psychologist Tony Buzan in the 1970s, mind mapping is based on research into how the brain processes and stores information. Buzan discovered that our minds work more effectively when we combine words, images, colors, and spatial relationships rather than relying on linear text alone.
The Science Behind Mind Mapping
Research from cognitive psychology supports the effectiveness of mind mapping. According to studies published in the Journal of Educational Psychology, visual learning techniques like mind mapping activate both hemispheres of the brain simultaneously. The left hemisphere processes the logical, sequential information while the right hemisphere handles the visual, spatial, and creative elements.
Neuroscience research has shown that our brains are naturally wired for pattern recognition and associative thinking. Mind maps capitalize on these innate abilities by presenting information in a format that aligns with our neural architecture.
Key Features of Mind Maps
Understanding the fundamental components of mind maps is essential for creating effective visual representations of information.
Central Topic: The main idea or subject is placed prominently in the center of the map, serving as the focal point from which all other information radiates. This central positioning reflects the importance of the core concept and creates a visual hierarchy that guides the reader’s attention.
Branches: Main themes extend outward from the central topic like spokes on a wheel. These primary branches represent the major categories or subtopics related to your central concept. Each branch should be clearly labeled and distinctly colored to create visual separation.
Sub-branches: Detailed information connects to the main branches, creating multiple levels of information hierarchy. These secondary and tertiary branches allow for increasingly specific details while maintaining the overall structure and flow of information.
Keywords: Rather than using complete sentences, mind maps utilize concise terms and phrases to represent ideas. This approach reduces cognitive load and makes scanning and reviewing information more efficient. The principle of chunking from cognitive psychology supports this approach.
Visual Elements: Colors, icons, symbols, and images enhance understanding and memory retention. Visual elements tap into our brain’s powerful image processing capabilities, making information more memorable and engaging. Studies from the Picture Superiority Effect demonstrate that we remember visual information far better than text alone.
The Comprehensive Benefits of Mind Mapping
Mind mapping offers numerous advantages across various applications, from education and business to personal development and creative projects.
Enhanced Visual Organization: Mind maps help reveal relationships between concepts that might not be apparent in traditional linear formats. The spatial arrangement of information creates a visual hierarchy that makes complex topics more comprehensible. Research from Stanford University shows that visual organization significantly improves comprehension and analysis skills.
Improved Memory Retention: The combination of visual, spatial, and verbal elements in mind maps creates multiple memory pathways, leading to better recall. The dual coding theory by Allan Paivio explains how combining verbal and visual information strengthens memory formation.
Stimulated Creative Thinking: Mind mapping encourages non-linear thinking and free association, which are essential for creativity and innovation. The branching structure allows ideas to flow naturally and often leads to unexpected connections and insights. Creative thinking research supports the value of associative thinking in generating novel solutions.
Efficient Information Processing: Mind maps provide an at-a-glance overview of complex topics, making them excellent tools for quick reference and review. The hierarchical structure allows readers to grasp both the big picture and specific details simultaneously.
Adaptive and Flexible Format: Unlike rigid document structures, mind maps are easily updated, expanded, and reorganized as understanding evolves. This flexibility makes them ideal for dynamic projects and iterative learning processes.
Improved Focus and Concentration: The process of creating mind maps requires active engagement with the material, leading to deeper processing and better understanding. Research on active learning demonstrates the superiority of engaged learning methods over passive information consumption.
Mind Mapping Applications Across Industries
Mind mapping has found applications across numerous fields and industries, demonstrating its versatility and effectiveness.
Education and Learning: Teachers and students use mind maps for lesson planning, note-taking, exam preparation, and project organization. Educational research consistently shows improved learning outcomes when visual methods are incorporated into instruction.
Business and Project Management: Companies utilize mind maps for strategic planning, brainstorming sessions, process mapping, and team collaboration. Popular project management methodologies like Agile and Scrum often incorporate visual thinking tools.
Software Development: Developers use mind maps for system architecture planning, feature mapping, and problem-solving. The visual nature helps teams understand complex relationships between different system components.
Healthcare and Therapy: Mental health professionals employ mind mapping as a therapeutic tool to help clients explore thoughts, feelings, and behavioral patterns. Cognitive behavioral therapy often incorporates visual mapping techniques.
Personal Development: Individuals use mind maps for goal setting, career planning, decision-making, and life organization. The visual format helps clarify priorities and identify action steps.
Digital Mind Mapping Tools and Technologies
The digital revolution has transformed mind mapping from a pen-and-paper exercise to a sophisticated digital practice with numerous software options available.
Popular Mind Mapping Software:
- MindMeister offers cloud-based collaboration features and integrates with popular productivity tools
- XMind provides advanced formatting options and supports multiple map structures
- Lucidchart combines mind mapping with flowchart and diagram capabilities
- SimpleMind offers cross-platform synchronization and intuitive design
- Coggle specializes in collaborative online mind mapping with real-time editing
Integration with Productivity Ecosystems: Modern mind mapping tools integrate seamlessly with popular productivity platforms like Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and Notion, creating comprehensive workflow solutions.
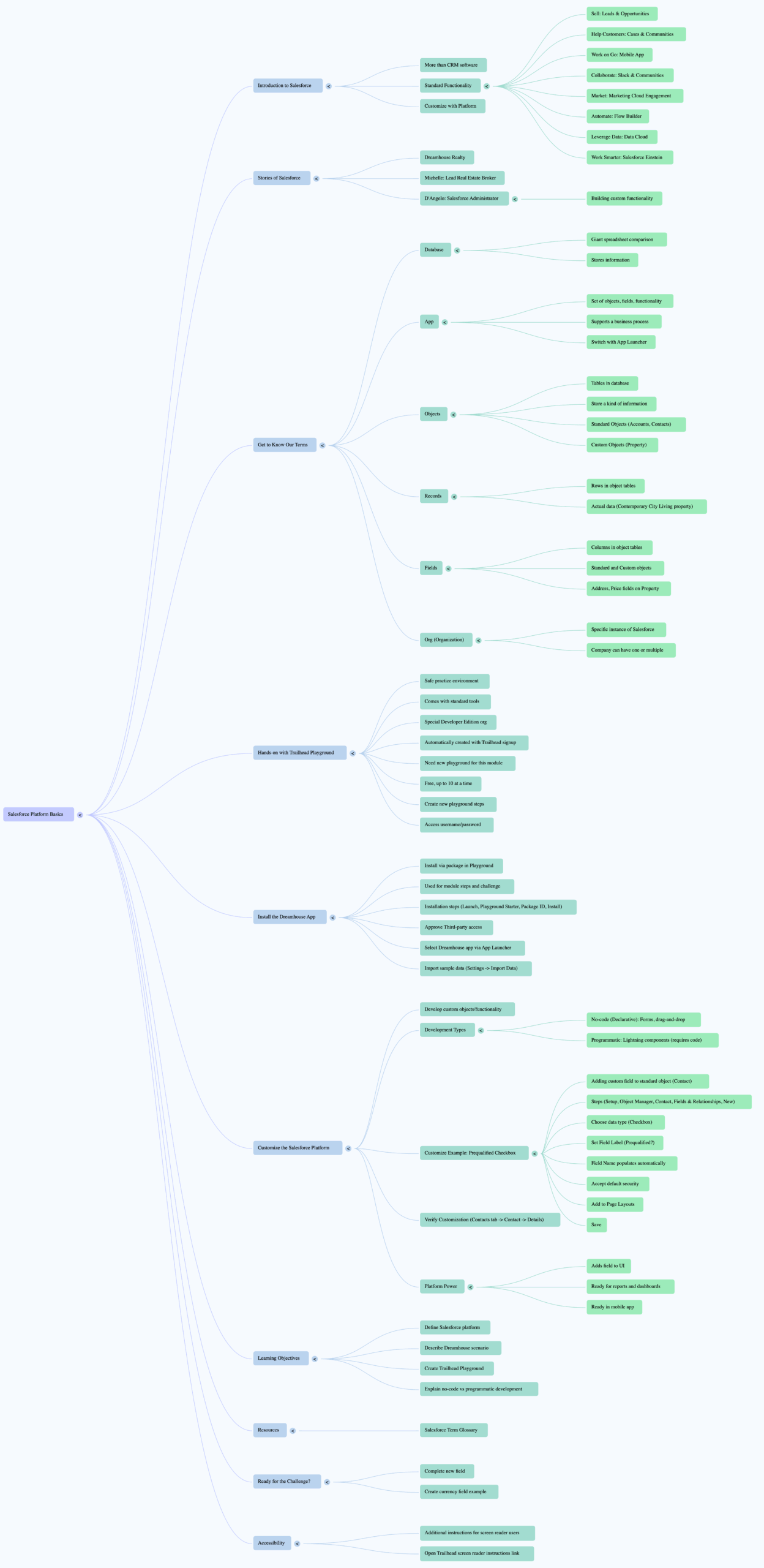
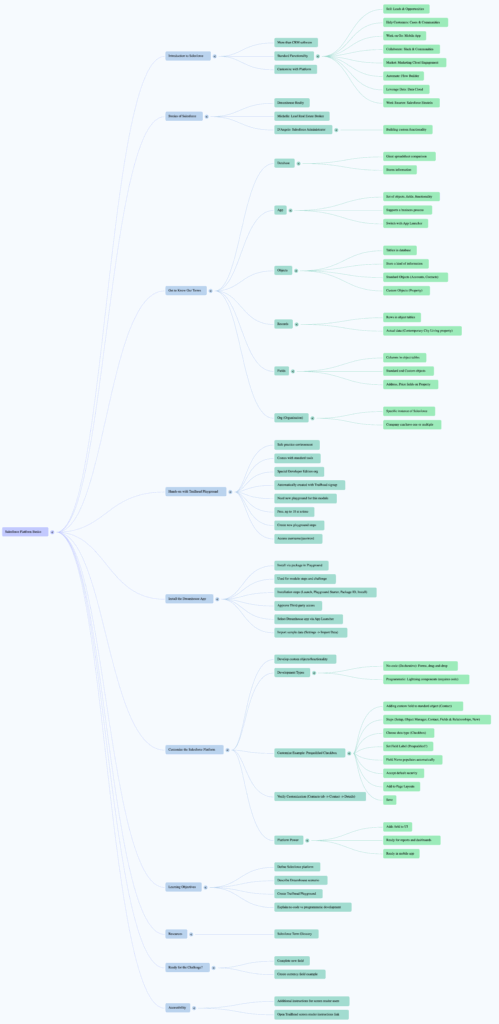
Mind Mapping for Salesforce Administrators
For Salesforce Administrators specifically, mind mapping serves as an invaluable tool for organizing the complex ecosystem of responsibilities, tools, and knowledge areas required for success in the role.
A comprehensive Salesforce Administrator mind map might include branches for:
Technical Skills: Configuration, customization, data management, security, automation, and integration capabilities. The Salesforce Trailhead platform provides structured learning paths that can be effectively organized using mind mapping techniques.
Business Processes: Understanding sales cycles, marketing automation, customer service workflows, and reporting requirements across different departments and use cases.
Stakeholder Management: Mapping relationships between different user groups, their specific needs, and how Salesforce solutions address various business challenges.
Continuous Learning: Organizing the vast array of Salesforce features, updates, and best practices in a visual format that makes ongoing education more manageable and systematic.
Best Practices for Effective Mind Mapping
Creating powerful mind maps requires following established principles and techniques that maximize their effectiveness.
Start Simple: Begin with your central topic and add branches gradually. Resist the temptation to include everything at once. The iterative approach allows for better organization and prevents overwhelming complexity.
Use Colors Strategically: Assign specific colors to different categories or themes to create visual consistency and aid in navigation. Color psychology research shows that strategic color use enhances memory and comprehension.
Keep Keywords Concise: Use single words or short phrases rather than complete sentences. This approach maintains clarity and makes scanning more efficient while reducing visual clutter.
Incorporate Visual Elements: Add icons, symbols, and small images to reinforce concepts and create memorable associations. Visual elements should support, not distract from, the core information.
Maintain Logical Hierarchy: Organize information from general to specific, ensuring that the relationship between parent and child branches is clear and logical.
Review and Refine: Regularly update and improve your mind maps as your understanding evolves. The dynamic nature of mind maps is one of their greatest strengths.
The Future of Mind Mapping
As technology continues to evolve, mind mapping is becoming increasingly sophisticated and integrated with emerging technologies.
Artificial Intelligence Integration: Modern mind mapping tools are beginning to incorporate AI capabilities that can suggest connections, auto-generate branches, and provide intelligent content recommendations.
Virtual and Augmented Reality: Emerging VR and AR technologies are creating immersive mind mapping experiences that allow users to navigate and manipulate information in three-dimensional space.
Collaborative Intelligence: Advanced collaboration features enable teams to co-create mind maps in real-time, fostering collective intelligence and distributed problem-solving capabilities.
Getting Started with Mind Mapping
Whether you choose traditional pen-and-paper methods or digital tools, the key to successful mind mapping lies in consistent practice and experimentation. Start with simple topics and gradually tackle more complex subjects as you develop proficiency with the technique.
Consider joining online communities like the International Mind Mapping Association or exploring resources from thought leaders in visual thinking and knowledge management. The Visual Thinking community offers additional insights and techniques for expanding your visual literacy skills.
Mind mapping represents a fundamental shift from linear to associative thinking, unlocking creative potential and improving information processing efficiency. By embracing this powerful visual thinking tool, you can transform how you learn, plan, solve problems, and communicate complex ideas in our increasingly information-rich world.
The journey of mastering mind mapping is itself a perfect subject for a mind map—start with the central concept of “learning mind mapping” and let your branches grow naturally as you explore this transformative thinking tool.